vs-secrets
1.2.1
See the version list below for details.
dotnet tool install --global vs-secrets --version 1.2.1
dotnet new tool-manifest # if you are setting up this repo dotnet tool install --local vs-secrets --version 1.2.1
#tool dotnet:?package=vs-secrets&version=1.2.1
nuke :add-package vs-secrets --version 1.2.1
Visual Studio Solution Secrets
Synchronize Visual Studio solution secrets across different development machines.
- Get Started
- Best Practices
- The Problem
- The Solution
- How to install
- Configure the encryption key and authorizations
- Push solution secrets
- Pull solution secrets
- Utility commands
- Configuration files
Get Started
If you already know it, here are the quick start commands.
dotnet tool install --global vs-secrets
vs-secrets init -p <your-passphrase>
vs-secrets pull
Best Practices
As a good practices in DevOps, you must not store secrets (sensitive data like passwords, connection strings, access keys, etc.) in your source code that is committed in a shared repository and secrets must not be deployed with the apps.
Fortunately Visual Studio and .Net help us in separating secrets from our code with the User Secrets Manager that let us store secrets out of the solution folder. The User Secrets Manager hides implementation details, but essentially it stores secrets in files located in the machine's user profile folder.
You can find the User Secrets Manager documentation here.
The Problem
The User Secrets Manager is a great tool, but when you change your development machine, usually you clone your project code from a remote repository and then you would like to be up and running for coding and testing in a matter of seconds.
But if you have managed secrets with the User Secrets Manager you will not be immediatly able to test your code because you will miss something very important on your new machine: the secret settings that let your code work.
The Solution
For being ready to start coding and testing on the new development machine, you have three choices.
- Manually copy secret files from the old machine to the new one, if you still have access to the old machine.
- Recreate the secret settings on your new machine for each project of the solution, but this can be tedious because you have to recover passwords, keys, etc. from different resources and it can be time consuming.
- **New** : use Visual Studio Solution Secrets to synchronize secret settings through the cloud in a quick and secure way.
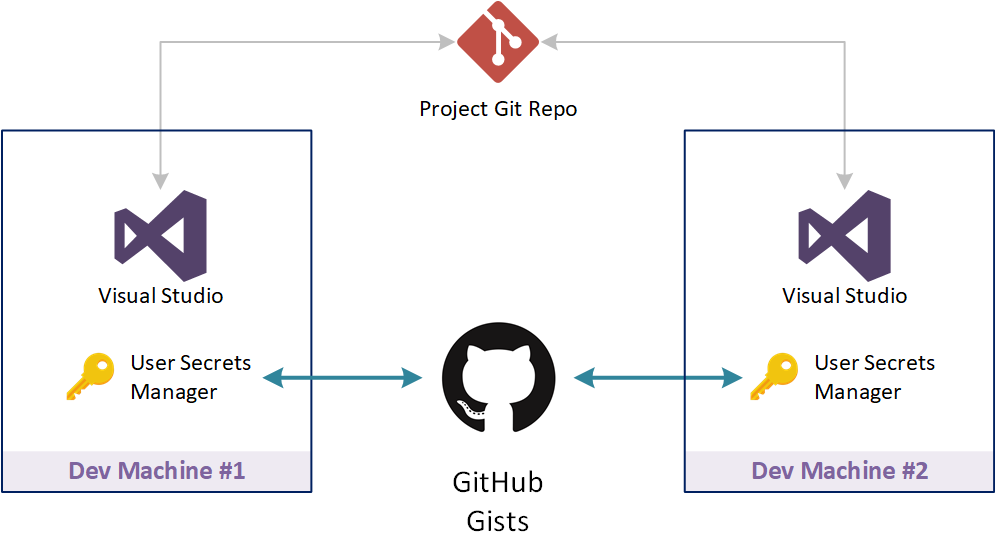
The idea is to use GitHub Gists as the repository for your secrets. Visual Studio Solution Secrets collects all the secret settings used in the solution, encrypts and pushes them on your GitHub account in a secret Gist, so that only you can see them. The encryption key is generated from a passphrase or a key file that you specify during the one time initialization phase of the tool.
Once you change the development machine, you don't have to copy any file from the old one.
Just install the tool, recreate the encryption key with your passphrase or your key file, authorize the tool on GitHub, pull the solutions secrets on your new machine and you are ready to code.
It's fast!
How to install
The tool is installed using the dotnet command line interface:
dotnet tool install --global vs-secrets
If you already have it, but you want to update to the latest version, use the command:
dotnet tool update --global vs-secrets
Configure the encryption key and authorizations
After the tool is installed, you need to create the encryption key and then authorize the use of your GitHub Gists.
Create the encryption key from a passphrase:
vs-secrets init -p <your-passphrase>
Otherwise, you can create the encryption key from a key file with the command below:
vs-secrets init --keyfile <file-path>
In case the encryption key is compromised you can change it.
vs-secrets changekey --passphrase <new-passphrase>
vs-secrets changekey --keyfile <file-path>
When you change the encryption key with one of the above commands, any secret already encrypted on GitHub is re-encrypted with the new key. In this way the compromised key becomes useless.
Push solution secrets
For pushing the secrets of the solution in current folder:
vs-secrets push
For pushing the secrets of the solution in another folder:
vs-secrets push --path <solution-path>
For pushing the secrets of all the solutions in a folder tree:
vs-secrets push --all
vs-secrets push --path <path> --all
Pull solution secrets
For pulling the secrets of the solution in current folder:
vs-secrets pull
For pulling the secrets of the solution in another folder:
vs-secrets pull --path <solution-path>
For pulling the secrets of all the solutions in a folder tree:
vs-secrets pull --all
vs-secrets pull --path <path> --all
Utility commands
Search for solutions that use secrets
You can use the tool for just searching solutions and projects that use secrets
vs-secrets search [--path <solution-path>] [--all]
Checking the status
The "status" command let you check for the status of the tool. The command below checks if the encryption key has been defined and if the tool has been authorized to access GitHub Gists:
vs-secrets status
If the current folder contains a solution, the "status command" will show also the synchronization status for the secrets of the solutions.
Optionally you can check the synchronization status in another folder using the --path parameter or in an entire folder tree adding the --all parameter. Here are some examples:
vs-secrets status --all
vs-secrets status --path c:\projects\my-project
vs-secrets status --path c:\projects --all
Configuration files
Visual Studio Solution Secrets stores its configuration files in the machine's user profile folder.
| Platform | Path |
|---|---|
| Windows | %APPDATA%\Visual Studio Solution Secrets |
| macSO | ~/.config/Visual Studio Solution Secrets |
| Linux | ~/.config/Visual Studio Solution Secrets |
The files generated by the tool are listed below.
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| cipher.json | Contains the encryption key |
| github.json | Contains the access token for managing user's GitHub Gists |
| Product | Versions Compatible and additional computed target framework versions. |
|---|---|
| .NET | net5.0 is compatible. net5.0-windows was computed. net6.0 is compatible. net6.0-android was computed. net6.0-ios was computed. net6.0-maccatalyst was computed. net6.0-macos was computed. net6.0-tvos was computed. net6.0-windows was computed. net7.0 was computed. net7.0-android was computed. net7.0-ios was computed. net7.0-maccatalyst was computed. net7.0-macos was computed. net7.0-tvos was computed. net7.0-windows was computed. net8.0 was computed. net8.0-android was computed. net8.0-browser was computed. net8.0-ios was computed. net8.0-maccatalyst was computed. net8.0-macos was computed. net8.0-tvos was computed. net8.0-windows was computed. |
| .NET Core | netcoreapp3.1 is compatible. |
This package has no dependencies.

